Conditional sentences have major role in daily conversation. Often we talk conditionally to each other. Giving condition and talking about the result. There are five main ways of constructing conditional sentences in English: (Conditional sentences type 1, type 2, type 3, zero conditional and mixed conditionals) In all cases, these sentences are made up of an if clause and a main clause. In this article we will look at Mixed Conditionals. You can read about the rest conditional sentences by clicking here.
Mixed Conditionals
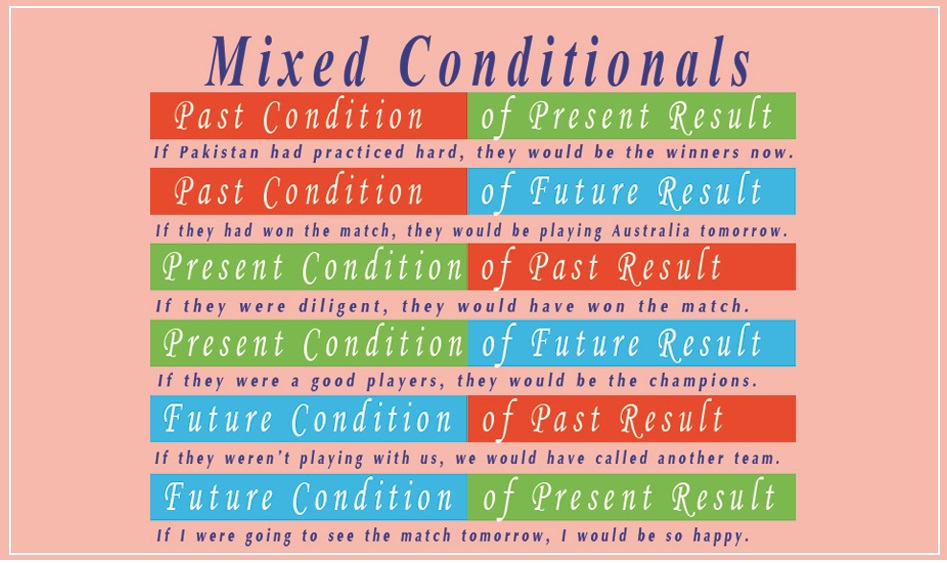
Mixed conditionals are those unreal conditional sentences whose time in the if-clause is different than the time in the main-clause. Learn about the rules of mixed conditionals below.
Past Condition of Present Result
If Clause/ Condition Result Clause/ Main Clause
(Past Perfect Tense) (Would + 1st V)
- If Pakistan had practiced hard, they would be the winners now.
But they didn’t practice hard and therefore they are the losers now. - If I had taken breakfast, I wouldn’t be so hungry.
But I didn’t take breakfast and therefore I am so hungry now.
Past Condition of Future Result
If Clause/ Condition Result Clause/ Main Clause
(Past Perfect Tense) (Would + 1st V/ ing form of verb)
- If you had informed us before, you would go to picnic with us today.
But you didn’t inform us before, and you are not going to picnic with us today. - If they had won the match, they would be playing Australia tomorrow.
But they lost the match and therefore they are not going to play Australia tomorrow.
Present Condition of Past Result
If Clause/ Condition Result Clause/ Main Clause
(Simple Past Tense) (Would have + Past Participle (3rd V))
- If they were diligent, they would have won the match.
But they are not diligent, and therefore they didn’t win the match. - If I didn’t have to complete my assignment, I would have gone to the party last night.
But I have to complete my assignment, and therefore I didn’t go the party last night.
Present Condition of Future Result
If Clause/ Condition Result Clause/ Main Clause
(Simple Past Tense) (Would + 1st V/ ing form of verb)
- If we didn’t have sufficient money, we would not buy a new house.
But we have sufficient money, and therefore we will buy a new house. - If Ali weren’t on vocation, he would be taking our English subject.
But Ali is on vocation, and therefore he is not going to take our English subject.
Future Condition of Past Result
If Clause/ Condition Result Clause/ Main Clause
(Past Continuous/ Simple Past) (Would have + Past Participle (3rd V))
- If they weren’t playing with us, we would have called another team.
But they are going to play with us, and therefore we didn’t call another team. - If it were raining tomorrow, we would have played the final yesterday.
But it is not going to rain tomorrow, and therefore we didn’t play the final yesterday.
Future Condition of Present Result
If Clause/ Condition Result Clause/ Main Clause
(Past Continuous/ Simple Past) (Would + 1st V)
- If I were going to the party tonight, I would be so happy.
But I am not going to the party, and therefore I am not happy. - If you didn’t go to the party tonight, everyone would be so disappointed.
But you are going to the party tonight, and therefore everyone is not disappointed.